Angular contact ball bearings are designed to withstand both radial loads and unidirectional or bidirectional axial loads.
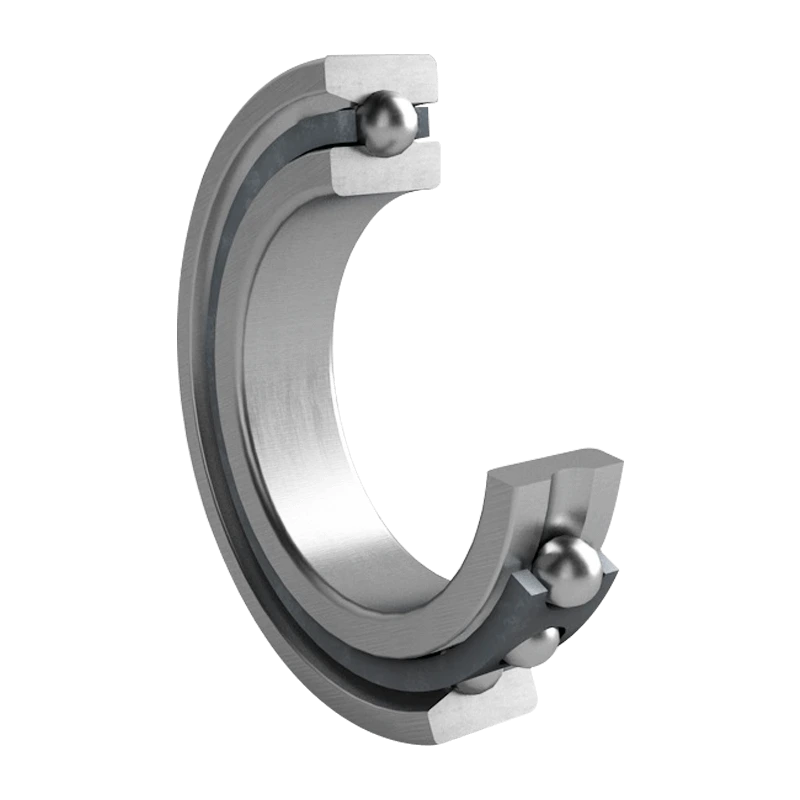

Contact Angle: The distinguishing feature of angular contact ball bearings is their contact angle, which is formed by the contact point between the inner and outer rings and the bearing axis. This angle varies from 15° to 40°, and the larger the angle, the stronger the axial load carrying capacity.
Single and Double Rows: These bearings can be single or double rows. The single row is suitable for carrying unidirectional axial loads, while the double row can carry bidirectional axial loads.
Ball & Groove Design: The contact surface between the ball and the inner and outer rings is curved, which allows the bearing to provide a larger contact area when bearing loads, thereby improving the load carrying capacity and service life.
Precision Instruments: Due to the precise manufacturing and high operational accuracy, they are widely used in precision instruments such as CNC machine tools.
Automotive Components: Commonly found in the steering and transmission systems of automobiles because they can effectively support and transfer loads.
Aerospace: It is also widely used in the aerospace industry due to its ability to operate stably at high speeds and variable loads.
Agricultural and Construction Machinery: Suitable for environments subjected to heavy loads and shock loads, such as axles for tractors and construction equipment.
High-Speed Performance: These bearings are typically designed for High-Speed applications and are structurally optimized to reduce friction and heat generation.
High Precision: Angular contact ball bearings are manufactured with high precision therefor they are suitable for high-demanding applications.
Adaptable to Different Loads: Different designs of contact angles to accommodate different axial and radial load combinations.
Multiple Sealing Forms: Open type, sealed type and shield type are available to adapt to different operating environments and maintenance needs.
Improve Operational Efficiency: The optimized design reduces internal friction and improves the overall efficiency of the machine.
Adapt to Complex Loads: Complex load combinations, including high axial and radial loads can be efficiently solved by selecting the right contact angle and design.
Enhance System Rigidity: Especially in high-speed and high-precision applications, the use of these bearings can improve the overall rigidity of the system.
Extended Service Life: High-quality manufacturing and design help bearings maintain performance in harsh environments, resulting in a longer service life.
● SKF (Sweden)
● NSK (Japan)
● FAG (Germany)
● NTN (Japan)
● Timken (USA)

Bearings are widely used in automobile engines, transmission systems, wheels and other critical components to support rotational motion and reduce friction.

In the energy industry, such as wind power, solar power and traditional power plants, bearings are used to support turbines, fans, generators and other equipment.

The field of heavy machinery manufacturing such as excavators, loaders, excavators, etc. Using bearings to support and rotate various moving parts.

Bearings are used in train and subway systems to support wheels and other moving components.

In marine and marine engineering, bearings are used to support ship engines, propellers, transmission systems, etc.

Bearings play a vital role in the design and operation of robotic arms. They not only ensure the smooth and precise movement of the robotic arm, but also have a direct impact on improving the performance, reliability and efficiency of the robotic arm.

Bearings are also often used in electronic equipment, such as computer hard drives, printers, and optical drives.
In medical equipment, such as scanners, X-ray machines, and surgical equipment, bearings are also be required.

The aerospace sector uses bearings to provide support in equipment such as aircraft landing gear, wing controls and satellite panels.
Call for online customer support get FREE BEARING SAMPLE
Online Quotation