Linear Guideway Bearings are mechanical components designed to provide linear motion while maintaining high precision, low friction and low wear. They are widely used in equipment that requires precise linear movement and offer numerous superior design fe
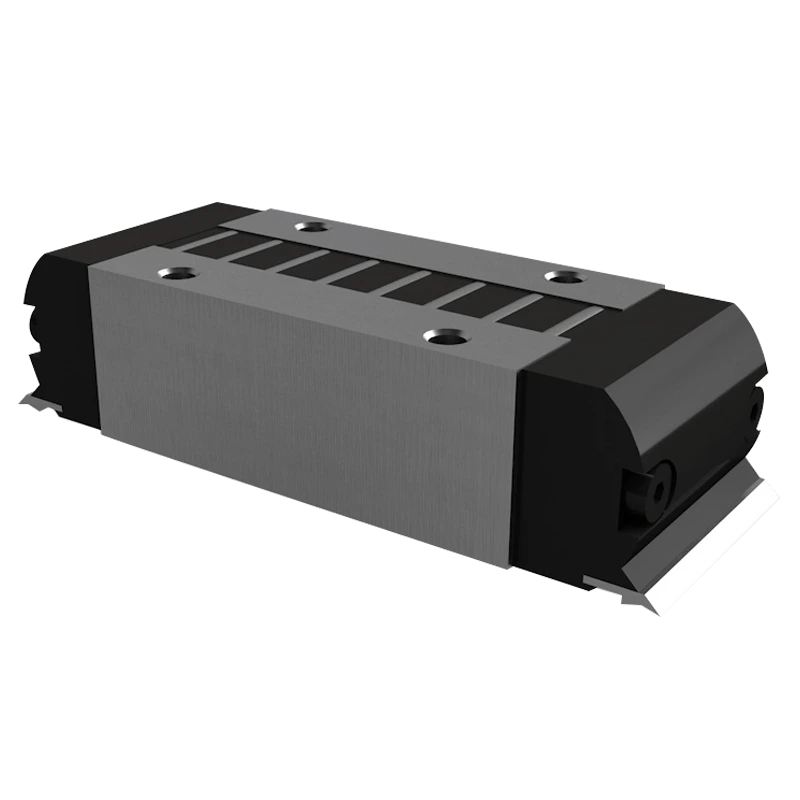

Linear guide bearings typically consist of the following main components:
Guide Rail: The guide rail is the foundation of the linear guide system, usually made of high-strength steel or other materials, ensuring smooth sliding and support capacity.
Slide Block: The slide block is the moving part of the guide rail, containing rolling elements (such as balls or rollers), which can provide low friction and high load capacity. The slide block makes contact with the guide rail and is responsible for sliding along it.
Rolling Elements: The rolling elements, such as balls or rollers, roll between the guide rail and the slide block, carrying the load and providing low friction.
Seals: To prevent dust and dirt from entering and affecting the sliding performance, linear guide bearings are usually equipped with seals or dust covers to extend service life.
Lubrication System: Most linear guide bearing systems are equipped with a lubrication mechanism to reduce friction and enhance durability.
The application range of linear guide bearings is very broad, especially in environments that require high precision and smooth linear motion. Typical application environments include:
CNC Machine Tools: In precision machining equipment such as CNC lathes, milling machines, and grinding machines, linear guides are used to ensure precise motion of the spindle and workpiece.
Industrial Robots: Linear guide bearings are used to provide smooth and precise linear motion for robotic arms.
Automated Production Lines: Automated equipment requiring smooth and high-precision linear motion can be supported by linear guide bearings.
Measuring Equipment: Such as Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) and laser measuring systems, which require very high positioning accuracy and stability.
Medical Equipment: In medical imaging equipment and automated testing equipment, linear guide bearings provide precise position control and motion stability.
Packaging and Conveying Systems: In packaging and conveying systems, linear guide bearings are used to ensure smooth handling and transport of items.
Low Friction and High Load Capacity: Linear guide bearings usually use rolling contact designs (such as balls or rollers), which significantly reduce friction, allows higher loads and longer service life.
High Precision: Through precision machining, linear guide bearings can provide high-precision linear motion, minimize errors and deviations.
Good Rigidity: Linear guide systems offer excellent rigidity, maintaining stability under high loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Easy Installation and Maintenance: Linear guides generally have standardized sizes and structures, making the installation process relatively simple and maintenance and lubrication easy to perform.
Self-Lubricating Design: Some linear guide bearings feature a self-lubricating design, reducing the need for external lubrication systems, which is particularly beneficial for applications in specialized environments.
High Precision and Stability: Linear guide bearings provide high precision linear motion, which can meet the needs of various high-precision processing and automation equipment.
Lower Friction and Wear: With the use of rolling elements, linear guide bearings have a relatively low friction coefficient, reducing energy consumption and extending the system's service life
High Load Capacity and Rigidity: Linear guides offer a high load capacity, and can maintain stable motion even under heavy loads.
Strong Adaptability: Linear guide bearings are suitable for various working environments and conditions, including high and low temperatures, humidity, and pollution. They often feature dust-proof, waterproof, and corrosion-resistant functions.
Reduced Vibration and Noise: Compared to sliding guides, linear guide bearings provide smoother motion, reducing vibration and noise, thereby enhancing the comfort of the working environment.
● THK (Japan)
● HIWIN (Taiwan)
● NSK (Japan)
● SKF (Sweden)
● FAG (Germany)
● IKO (Japan)
● Schneeberger (Switzerland)
● Rollon (Italy)

Bearings are widely used in automobile engines, transmission systems, wheels and other critical components to support rotational motion and reduce friction.

In the energy industry, such as wind power, solar power and traditional power plants, bearings are used to support turbines, fans, generators and other equipment.

The field of heavy machinery manufacturing such as excavators, loaders, excavators, etc. Using bearings to support and rotate various moving parts.

Bearings are used in train and subway systems to support wheels and other moving components.

In marine and marine engineering, bearings are used to support ship engines, propellers, transmission systems, etc.

Bearings play a vital role in the design and operation of robotic arms. They not only ensure the smooth and precise movement of the robotic arm, but also have a direct impact on improving the performance, reliability and efficiency of the robotic arm.

Bearings are also often used in electronic equipment, such as computer hard drives, printers, and optical drives.
In medical equipment, such as scanners, X-ray machines, and surgical equipment, bearings are also be required.

The aerospace sector uses bearings to provide support in equipment such as aircraft landing gear, wing controls and satellite panels.
Call for online customer support get FREE BEARING SAMPLE
Online Quotation