Self-aligning bearings are a type of bearing designed to accommodate mounting errors or shaft deflection and are ideal for situations where the mounting base may be uneven or the shaft may be bent.
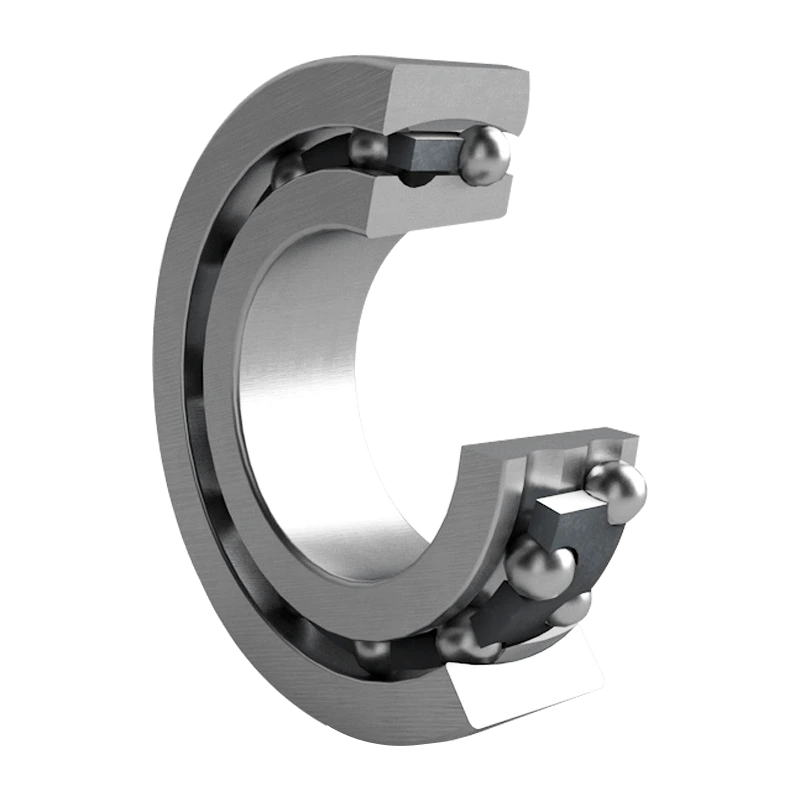

Two Main Types: There are two types of self-aligning bearings, namely self-aligning ball bearings and self-aligning roller bearings. Ball bearings use spherical rolling elements, while roller bearings use strip or barrel rollers.
Highly Adaptable: Self-aligning bearings can work under imperfect conditions, automatically adjusting to accommodate deviations in the axis.
Inner Ring Design: The inner ring can be available in two designs: a single inner ring with two spherical raceways or two independent inner rings, allowing for a greater degree of freedom and higher load carrying capacity.
Construction Machinery: In construction equipment, such as tower cranes and overhead cranes, bearings often need to be adjusted to accommodate the movement and deformation of the structure.
Paper and Textile Machinery: The machines in these industries, bearings need to accommodate shaft deflection due to long operating hours.
Wind Turbines: Bearings in wind turbines need to be able to accommodate irregular loads and bent shafts.
Reduced Maintenance Requirements and Increased Operational Efficiency: Self-aligning bearings reduce maintenance requirements and increase operational efficiency in applications where bearings are heavily loaded but mounted on unstable foundations, such as mining equipment, metallurgical equipment, etc.
Automatic Alignment Capability: Able to compensate for imperfect alignment due to mounting errors or shaft bending.
Accommodating Different Load Conditions: Designed to handle different load types, including high radial loads and medium axial loads.
Reduced Friction and Wear: The self-aligning design reduces internal friction and thus extends the life of the bearing.
Ease of Maintenance: Due to its ability to combat installation inaccuracies, it reduces the need for precise installation and adjustment.
Alignment Errors: Addresses alignment issues caused by mounting errors or shaft deformation during use.
Withstand Complex Loads: Adaptable to stable operation under variable load conditions, especially when the load direction may change.
Simplified Installation Process: The installation process is easier and faster due to the self-centering function, reducing the need for high-precision installation skills.
Reduced Maintenance Costs: Improves overall equipment operational efficiency and reliability by reducing mechanical breakdowns and downtime.
● SKF (Sweden)
● NSK (Japan)
● FAG (Germany)
● NTN (Japan)
● Timken (USA)

Bearings are widely used in automobile engines, transmission systems, wheels and other critical components to support rotational motion and reduce friction.

In the energy industry, such as wind power, solar power and traditional power plants, bearings are used to support turbines, fans, generators and other equipment.

The field of heavy machinery manufacturing such as excavators, loaders, excavators, etc. Using bearings to support and rotate various moving parts.

Bearings are used in train and subway systems to support wheels and other moving components.

In marine and marine engineering, bearings are used to support ship engines, propellers, transmission systems, etc.

Bearings play a vital role in the design and operation of robotic arms. They not only ensure the smooth and precise movement of the robotic arm, but also have a direct impact on improving the performance, reliability and efficiency of the robotic arm.

Bearings are also often used in electronic equipment, such as computer hard drives, printers, and optical drives.
In medical equipment, such as scanners, X-ray machines, and surgical equipment, bearings are also be required.

The aerospace sector uses bearings to provide support in equipment such as aircraft landing gear, wing controls and satellite panels.
Call for online customer support get FREE BEARING SAMPLE
Online Quotation